General-purpose computers
A general-purpose computer is a computer that is designed to be able to carry out many different tasks. Desktop computers and laptops are examples of general-purpose computers. Among other things, they can be used to:
access the internet
browse the world wide web (WWW)
use word processing software
play games
communicate via email and social media
design and build web pages
store and retrieve data
play videos and music
Each of these tasks is called an application. Any computer that can have many applications, such as those listed, is a general-purpose computer.
Apart from desktop computers and laptops, the following devices are also general-purpose computers:
tablets – like desktop computers, they can run a variety of applications
smartphones – today’s smartphones can also run a variety of applications
games consoles – as well as games, modern consoles also enable users to watch videos, play music, and browse the internet
media systems in cars – allow users to navigate, listen to music and connect to a smartphone
Hardware and software
General-purpose computers consist of hardware and software. Hardware is the physical components of the computer, such as the central processing unit (CPU), hard disk, monitor, keyboard, and mouse. Software is the programs that run on a computer.
Hardware is the physical component of a computer. Software is the programs that run on a computer.
The general-purpose computer model
All general-purpose computers follow the same basic model.
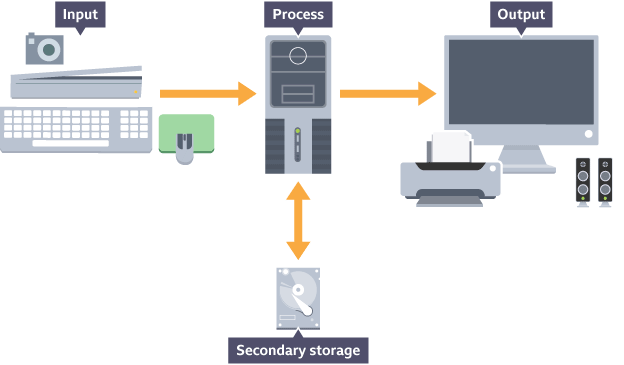
This diagram illustrates the flow of data within a desktop computer. Data is input, processed, then either output or sent to secondary storage. It is held in the main memory while it is being processed.
The CPU receives instructions and data from an input or memory. The instructions and data are processed by the CPU and the results are either sent to output or transferred to secondary storage.
Input is from an input device such as a keyboard, mouse, camera, or scanner. Output is to an output device, such as a monitor, printer or speaker.
THE CPU processes data/instructions and controls the computer system.
The purpose of the CPU
The CPU is the most important hardware component in a computer. It has two main functions:
to process data and instructions
to control the rest of the computer system
All programs and data processing is run in the CPU and all hardware components are, to some extent, controlled by it.
The Input-process-output model:
A computer is a machine that takes some kind of input from its surroundings, processes the input according to given rules, and provides some kind of output.
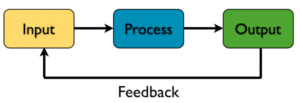
You are probably familiar with a desktop computer. The keyboard provides input and the screen provides output (which depends on what you type). In a similar way, the embedded computer in a washing machine has controls that provide input and a motor and heater as outputs; how fast they spin and how much heat they produce depends on the input setting.
The clever bit in computer science is the activity that goes on between the inputs and outputs – the processing. Processing means performing a series of actions on the inputs according to a given set of rules.
